Pregnancy and Plyometric Exercises for Power
1. Introduction
Pregnancy is a transformative journey, bringing immense joy and excitement alongside physical changes. While these changes are natural, they can also impact a woman's fitness routine. One area of concern is power, which can decline as the pregnancy progresses. Fortunately, plyometric exercises offer a solution. However, modifications and precautions are essential to ensure the safety of both mother and baby.
2. Understanding Plyometrics
2.1 Definition and Types
Plyometrics, also known as jump training, involves rapid stretching and contracting of muscles. These exercises utilize the body's natural stretch reflex to generate explosive power. Examples of plyometric exercises include box jumps, squat jumps, and depth jumps.
2.2 Benefits for Non-Pregnant Individuals
In non-pregnant individuals, plyometrics offer numerous benefits, including:
- Increased vertical jump height
- Improved sprint speed
- Enhanced agility and coordination
- Increased muscle strength and power
3. Modifications for Pregnancy
3.1 Safety Considerations
While plyometrics can be beneficial during pregnancy, it's crucial to prioritize safety. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise program, especially during pregnancy.
3.2 Safe Plyometric Exercises During Pregnancy
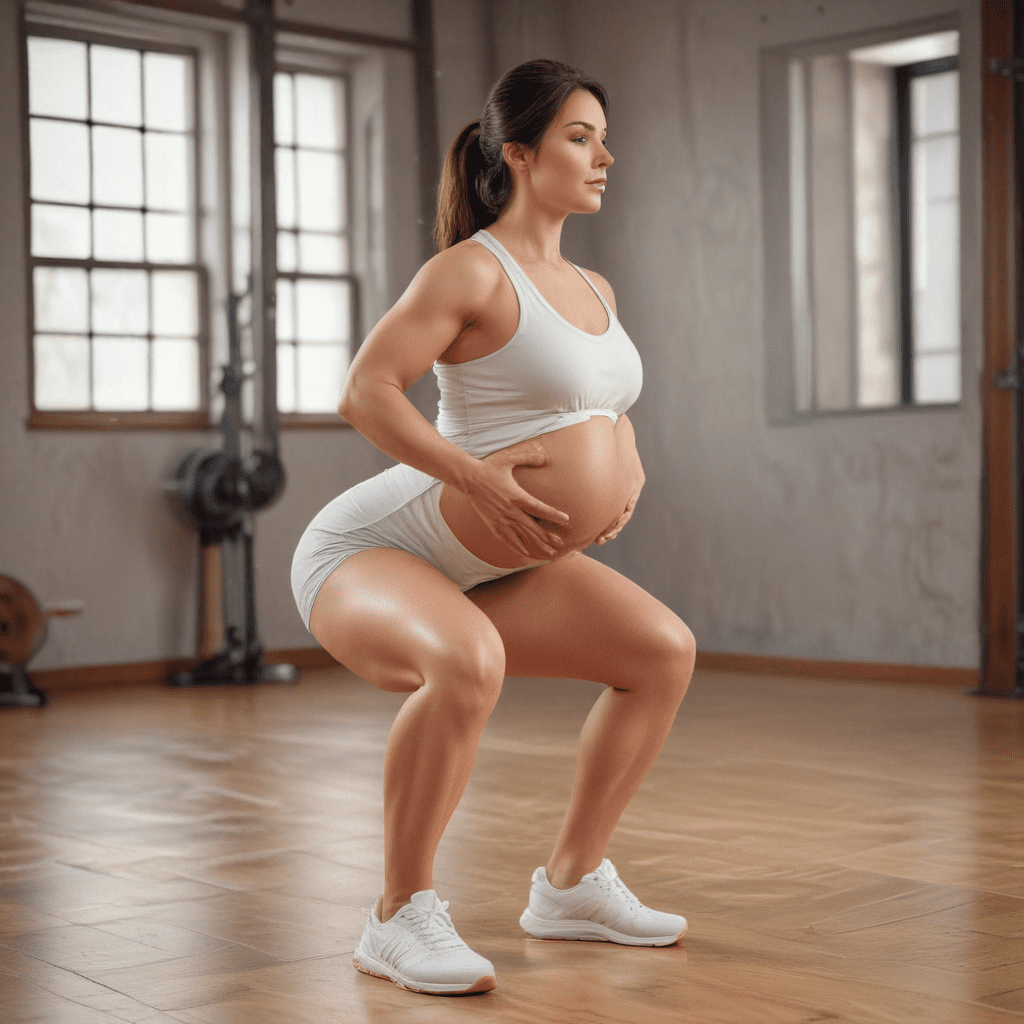
During pregnancy, certain plyometric exercises should be avoided, such as those with high impact or risk of falling. Here are some examples of safe plyometric exercises for pregnant women:
- Modified box jumps: Instead of jumping onto a box, step up and then step down.
- Squat jumps: Perform the exercise without jumping, focusing on lowering yourself down into a squat and then pushing back up.
- Depth jumps: Step off a low platform and simply land softly.
3.3 Trimester-Specific Modifications
Plyometric exercises should be modified according to the trimester of pregnancy.
- First trimester: Focus on lower-intensity exercises with minimal impact.
- Second trimester: Gradually increase the intensity and duration of the exercises.
- Third trimester: Reduce the intensity and focus on maintaining strength and power.
6. Cautions and Contraindications
While plyometrics can be beneficial during pregnancy, it's important to exercise caution and consider contraindications.
Cautions:
- Listen to your body: Pay attention to any discomfort or pain during exercise and adjust the intensity accordingly.
- Maintain hydration: Drink plenty of fluids before, during, and after exercise.
- Warm up and cool down: Always warm up before plyometric exercises and cool down afterward.
Contraindications:
- History of premature labor: If you have a history of premature labor, plyometric exercises may not be recommended.
- Placenta previa: This condition occurs when the placenta covers the cervix, preventing the baby from exiting the womb. Plyometrics may be contraindicated in this case.
- Preeclampsia: This is a serious pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure and other symptoms. Plyometrics are not recommended for women with preeclampsia.
7. Importance of Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Consulting with your healthcare provider before starting any plyometric exercise program during pregnancy is essential. They can assess your individual health and provide guidance on safe exercises and modifications.
8. Conclusion
While plyometric exercises can be beneficial during pregnancy, safety should be the top priority. By prioritizing safety, consulting with a healthcare professional, and making appropriate modifications, pregnant women can enjoy the benefits of plyometrics while ensuring the well-being of themselves and their babies.
9. References
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG). (2015). Exercise during pregnancy and the postpartum period. Committee Opinion No. 650.
10. FAQs
1. Are plyometric exercises safe during pregnancy?
With proper precautions and modifications, plyometric exercises can be safe for most pregnant women. However, it's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise program during pregnancy.
2. What are some of the benefits of plyometric exercises during pregnancy?
Benefits of plyometrics during pregnancy include improved strength and power, enhanced cardio-respiratory fitness, and a reduced risk of gestational diabetes.
3. What are some safe plyometric exercises for pregnant women?
Safe plyometric exercises for pregnant women include modified box jumps, squat jumps (without jumping), and depth jumps (stepping off a low platform).
4. What are the contraindications for plyometric exercises during pregnancy?
Contraindications for plyometric exercises during pregnancy include a history of premature labor, placenta previa, and preeclampsia.
5. How often should I do plyometric exercises during pregnancy?
The frequency of plyometric exercises during pregnancy will vary depending on your individual fitness level and health. Start with a low frequency and gradually increase as you become more comfortable.